The Microbiome & What it Means to Us
The Human Microbiome is an Eco-System:
Our Microbiome is an “ecological community of symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms” found in and on all multicellular organisms studied to date from plants to animals. The microbes includes bacteria, archaea, fungi and viruses.
Many kinds of eco-systems including David Latimer’s sealed terrarium that he first planted 53 years ago and has not been watered since 1972 yet continues to thrive in its sealed environment.
Microbes are the oldest forms of life on earth:
Researchers at UCLA and the University of Wisconsin–Madison have confirmed that microscopic fossils discovered in a nearly 3.5 billion-year-old piece of rock in Western Australia are the oldest fossils ever found and indeed the earliest direct evidence of life on Earth. [https://news.wisc.edu/oldest-fossils-found-show-life-began-before-3-5-billion-years-ago/]
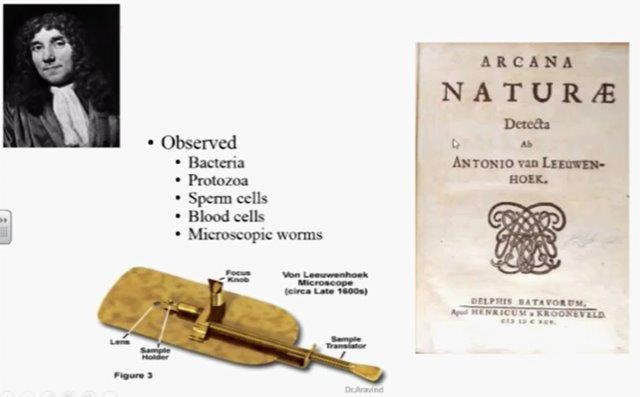
First Observation of Living Microbes:
Microorganisms are invisible to the human eye so we didn’t know they existed until the invention of the microscope. The smallest of bacteria is about .2 μm to the largest about 50 μm (micrometer = 1 millionth of a meter or one thousandth of a mm), Viruses can be as small as 100 nanometers. (one billionth of a meter or 1,000,000th of a mm)
First time any microorganisms were identified was by van Leeuwenhoek in 1683 who used single-lensed microscope of his own design. He analyzed some plaque from his teeth and wrote the above words to his colleges at The Royal Society. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as “the Father of Microbiology”.
The Human Microbiome
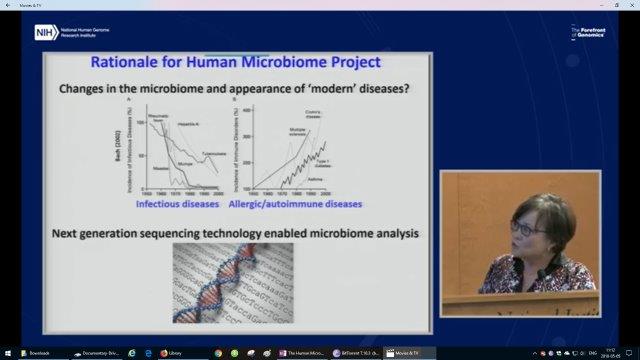
The Human Microbiome Project (HMP) was a United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) research initiative to improve understanding of the microbial flora involved in human health and disease. Launched in 2008, the first phase (HMP1) was a five-year project that focused on identifying and characterizing human microbial flora. The second phase, known as the Integrative Human Microbiome Project (iHMP) launched in 2014 with the aim of generating resources to characterize the microbiome and elucidating the roles of microbes in health and disease states. The program received $170 million in funding by the NIH Common Fund from 2007 to 2016, with the iHMP closing in 2017. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_Microbiome_Project>
The decrease of Infectious Disease and increase of what is called modern diseases of Allergic & Autoimmune Diseases and the correlation to the human microbiome. This is one of the goals of the NIH funded Human Microbiome Project (HMP).
[The Human Microbiome Project – Lita Proctor]
[The Human Microbiome Project – Lita Proctor PPT Slides 2018-02-06]
The Microbiome
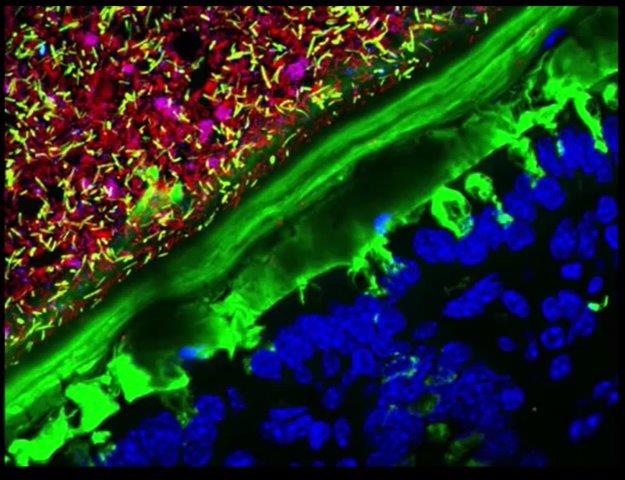
Erica Sonnenburg claims this is a real image (cross section of the colon stained with fluorescent probes) and won 2nd place at some Nikon Image Contest. The image shows the colon microbes on the upper left, the green layer is the gut mucus layer and the blue being human cells.
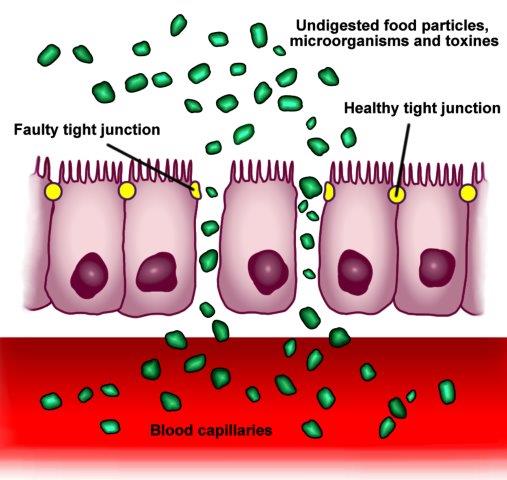
It is this mucus layer that protects the human cells from the microbes. Leaky Gut Syndrome is when this mucus layer becomes permeable and microbes infect human cells… [Disclaimer: Unlike the scientific phenomemon of increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”), claims for the existence of “leaky gut syndrome” as a distinct medical condition come mostly from nutritionists and practitioners of alternative medicine is a fad diagnosis using the alleged condition as an opportunity to sell a number of alternative-health remedies. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leaky_gut_syndrome>]
The opening of intercellular tight junctions (increased intestinal permeability) can allow passage of microbes, microbial products, and foreign antigens into the mucosa and the body proper. This can result in activation of the immune system and secretion of inflammatory mediators. Increased intestinal permeability is a factor in several diseases, but the cause–effect relationship between increased intestinal permeability in most of these diseases is not clear. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intestinal_permeability>
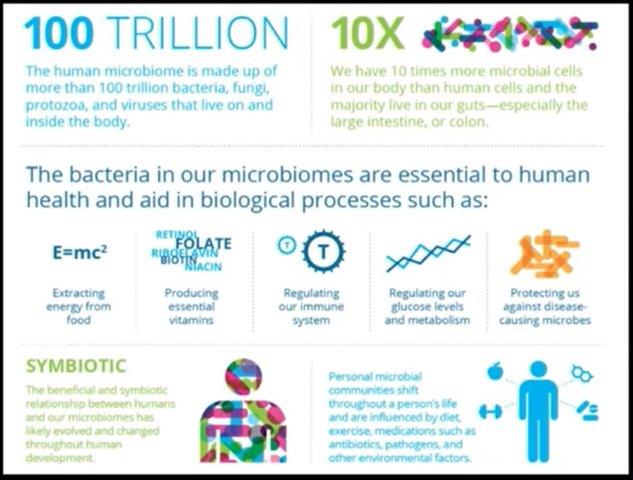
The microbiome is more than just a bunch of microorganisms living on our body and in our gut! It is integral to many of our organs, our Brain and crucial in our Immune System. This is brand new science that has only been possible since the extreme drop in costs for DNA sequencing:
– Adds 10 times more cells. (DNA)
– Adds 100 times more genes.
– Communicates and exchange molecules with human cells.
– Bonnie Bassler’s work shows that it communicates with itself and other microbes controlling various genes and activities called Quorum Sensing.
– It interreacts with our Immune System strengthening or weakening it.
– It helps us with processing foods like starches, fibers, grains and much more.
– It literally interacts with our genes to make us who we are.
– We share our microbiome in all the environments we interact with and amongst ourselves and our pets.
– There is much discussion about how and whether to treat the microbiome as another organ or organ system of the human body.

[Katherine Pollard Decoding the Human Microbiome] – 2016 Stanford School of Medicine
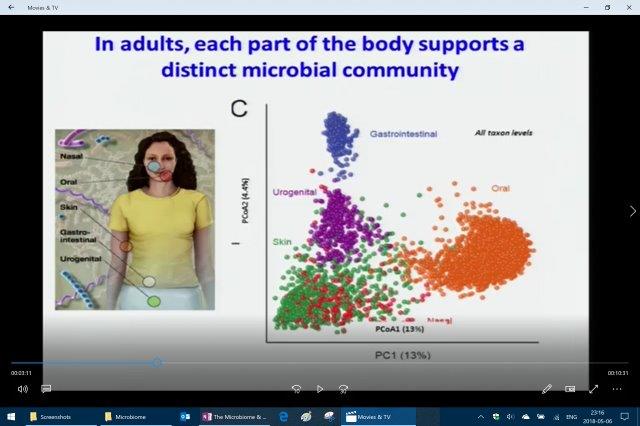
Like a finger print the Human Microbiome is totally unique to every individual, although sharing a large volume of species the difference between each of us is unique. Rob Knight’s lab has identified the microbiome of every person is unique and they can match a mouse and keyboard to the person by swabbing the keyboard in the well-known “Keyboard Study”.

[The Human Microbiome – Eric Alm, PhD, Martin Blaser, MD, John Cryan, PhD, Rob Knight, PhD] 2013 Eric Alm in a study “A Year in My Microbiome” tracked 300 different factors (everything they could think of significant enough to record and measure.)
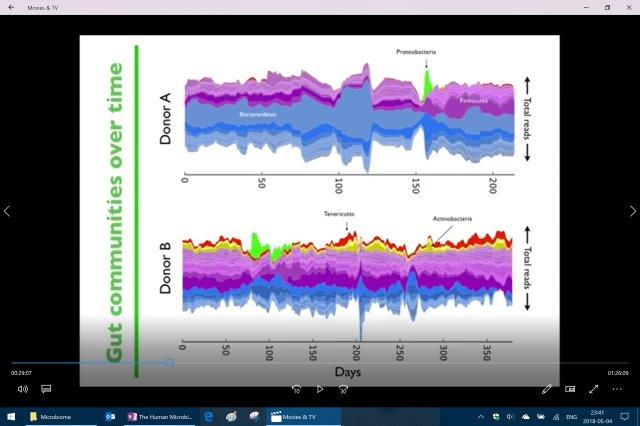
[Eric and his students microbiome analysis]
Interesting points he discusses here that even though the microbiome is very different between individuals and that the microbiome changes day-to-day it doesn’t really change that much month-to-month or year-to-year. That the microbiome is very stable over time to a degree. (Baby’s changes into and adult then into an elderly biome.)
The Microbiome & Human Health
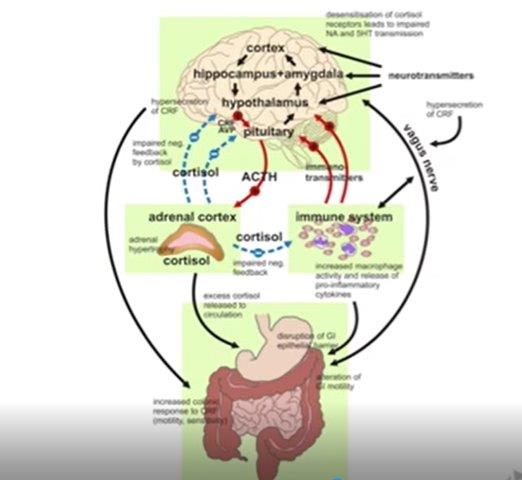
There appears to be strong connection between the Gut Microbes & Brain: Science is trying to better understand the effect on the brain, mood, cognition, emotion and perhaps visceral pain.
Problems are numerous:
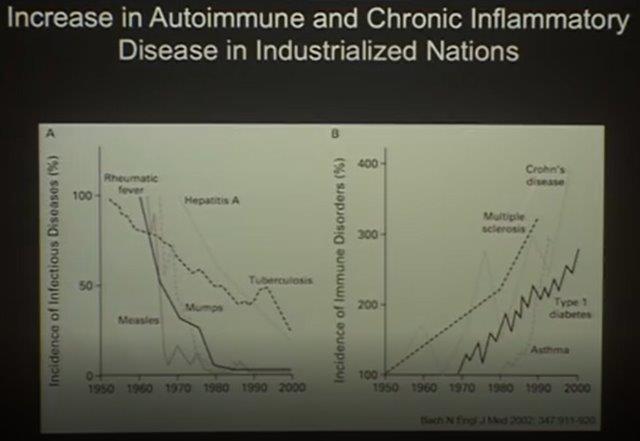
Lots of paper to point out the sharp decline of infectious diseases due to hygiene, vaccinations, and antibiotics simultaneously an equally sharp rise of autoimmune and chronic inflammation disease:
– Asthma
– Allergenic responses
– Crohn’s disease, Irritable Bowel Syndrome
– Type 1 & Type 2 diabetes (especially in young children)
– Multiple Sclerosis
– Obesity
Solutions:
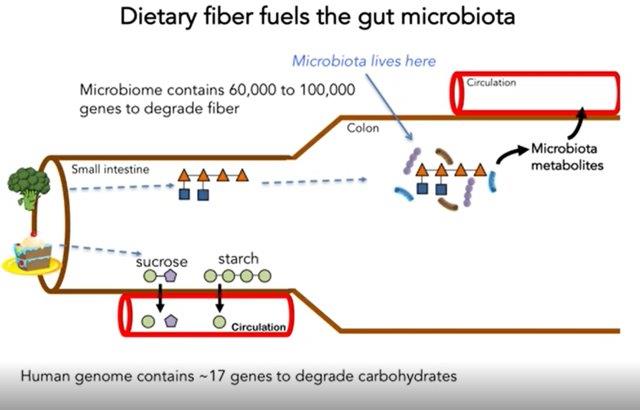
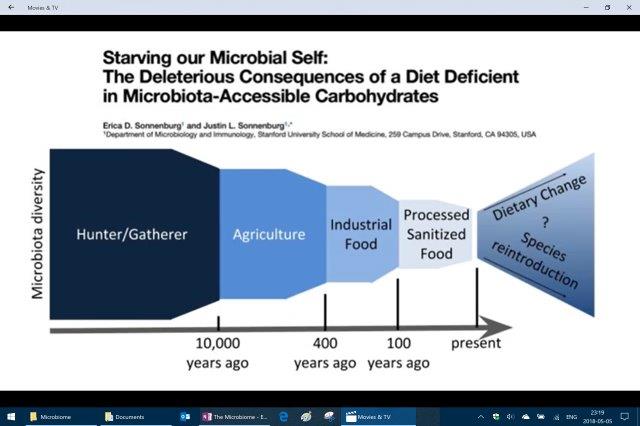
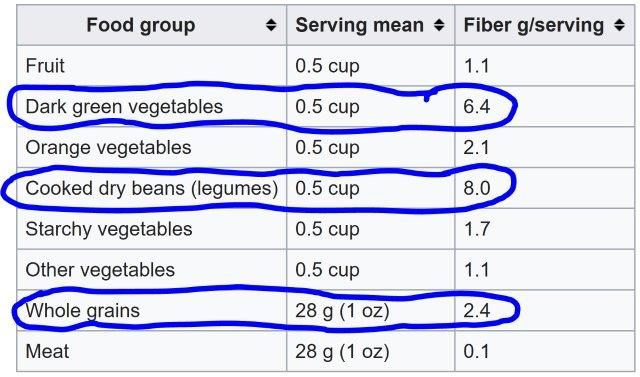
Dietary fiber or roughage is the indigestible portion of food derived from plants. It has two main components:[1]
-Soluble fiber, which dissolves in water, is readily fermented in the colon into gases and physiologically active by-products, and can be prebiotic and viscous. This delays gastric emptying which, in humans, can result in an extended feeling of fullness.
-Insoluble fiber, which does not dissolve in water, is metabolically inert and provides bulking, or it can be fermented in the colon. Bulking fibers absorb water as they move through the digestive system, easing defecation. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dietary_fiber>
Dietary fibers can act by changing the nature of the contents of the gastrointestinal tract and by changing how other nutrients and chemicals are absorbed. Some types of soluble fiber absorb water to become a gelatinous, viscous substance which may or may not be fermented by bacteria in the digestive tract. Some types of insoluble fiber have bulking action and are not fermented. Lignin, a major dietary insoluble fiber source, may alter the rate and metabolism of soluble fibers. Other types of insoluble fiber, notably resistant starch, are fermented to produce short-chain fatty acids. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dietary_fiber>
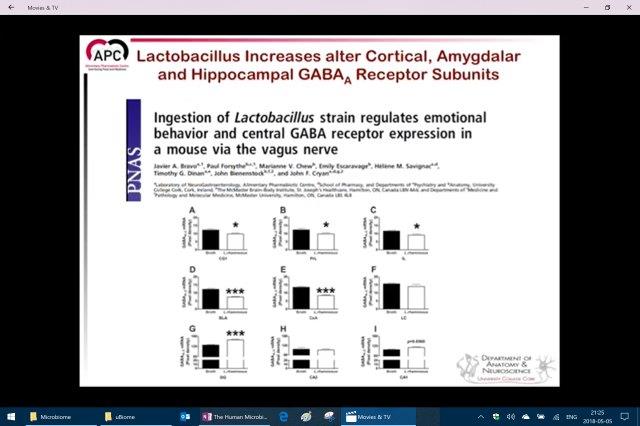
Probiotic (Lactobacillus) experiments in mice showed significant response over multiple tests.
Scientists Eric & Justin Sonnenburg’s strategy for their family’s health:
– They have increased the fiber in their diet.
– They built a nice vegetable garden in their front yard and encourage the kids to play in the dirt, eat the vegetable straigth from the plants.
– They have added a small family dog that is allowed in and out of the house, on the furniture, licking the kids, etc.
If worse comes to worse – Eat Shit!
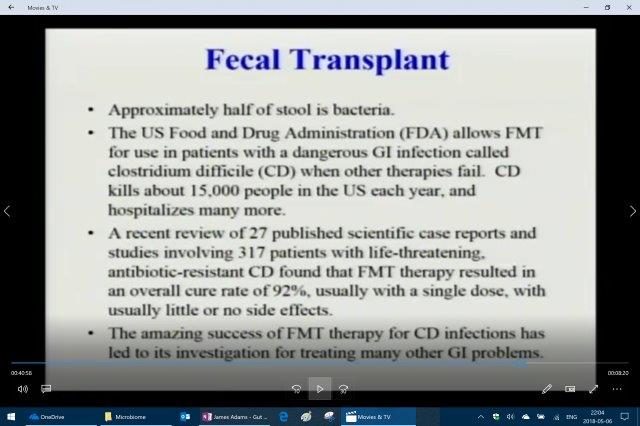
[Gut Bacteria, Diet, Essential Fatty Acids, Probiotics, and Fecal Transplants – James Adams, PhD]
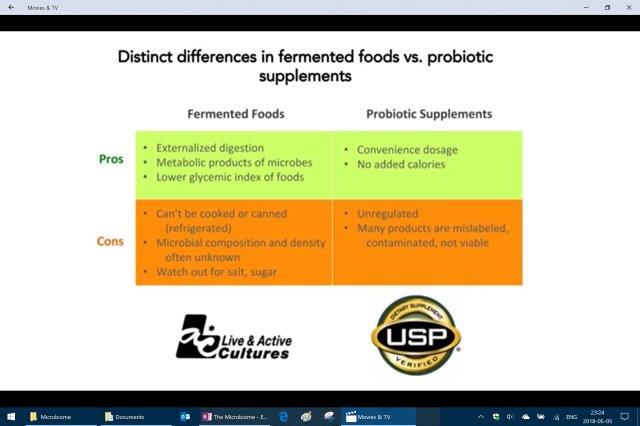
– Probiotics: (4 studies) Adams claims a little affect but hard to really quantify.
– Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT): 92% cure rate making it the most successful therapy for Clostridium Difficile (C-Diff or CD)
Fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), also known as a stool transplant, is the process of transplantation of fecal bacteria from a healthy individual into a recipient. FMT involves restoration of the colonic microflora by introducing healthy bacterial flora through infusion of stool orogastric tube or by mouth in the form of a capsule containing freeze-dried material from a healthy donor. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fecal_microbiota_transplant>
The results expressed by doctors and patient’s is simply amazing. Patient’s on their death bed after tons of antibiotic treatments, hospitalization, huge costs and suffering are cured permanently by eating a little shit from someone else. Almost no side effects, cheap, natural, easy and cured at the highest rate of any other medical therapy!
My Interest:
– Understanding our microbiome related to our health. (Daughter)
– Understanding our microbiome related to our environment. (The Built Environment)
– Understanding our microbiome related to where we live. (Are China microbes bad for us?)
Our Health:
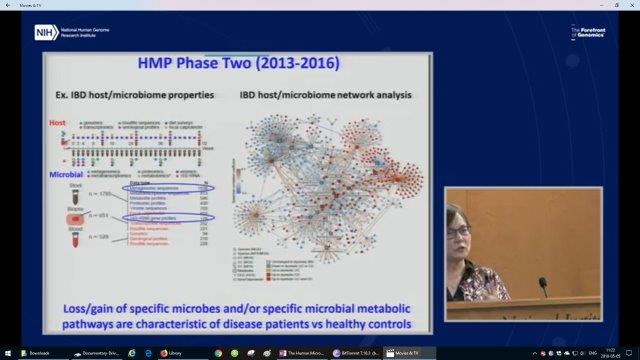
Part of the result of the HMP-2 was that the human microbiome is much more complex than previously understood but what became clear in this 10 Year Study is that the loss/gain of specific microbes and/or specific metabolic pathways are characteristic of diseased patients verses healthy patients suggesting the significant role our microbiome plays in health and disease.
Our Environment: The Built Environment
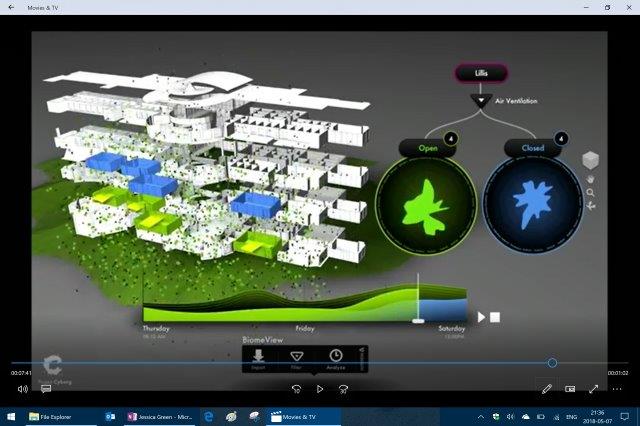
[Jessica Green Good germs make healthy buildings – TED Talk]
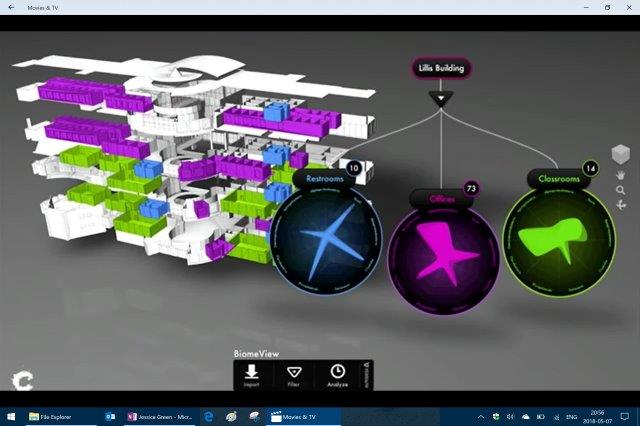
In collaboration with AutoDesk, Jessica’s lab sampled over 300 rooms in this building and built a model of the microbial composition. Interesting, and much like the body different rooms (bathrooms for example) share similar microbes but the microbial community from offices to classrooms, to bathrooms are distinct. Similar to the body where many sites have similar community but the different sites have their distinct communities.
Microbes are dispersed around by people and by air.
Jessica looked at the air handling units from different parts of the building and like the rooms, particular air handling units had same communities while the air handling unit in a different part of the building had a distinct community.
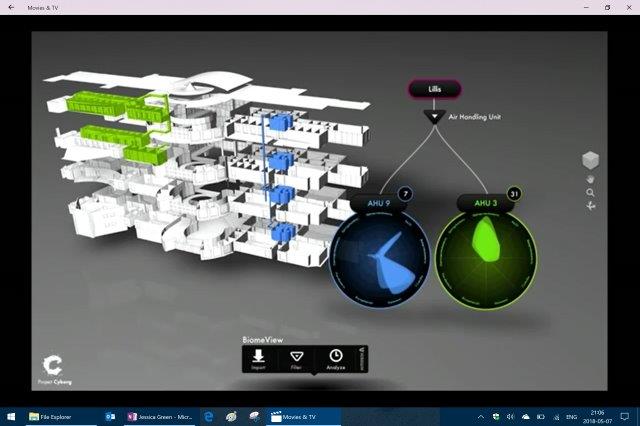
At this part of the talk Jessica describes comparing the microbial community to the outside air, building rooms that were blocked off from air ventilation at night compared with the day when air is being moved. The rooms that were blocked off when entered the next day had a strong smell and their data suggesting it was from leaving behind the air born bacteria soup from the people the day before.
Compare this to rooms with a ventilation system that allowed air in throughout the night they could see the microbial community tracked the outdoor air microbes much closer. The ventilation design helped washed away the buildings resident microbial landscape.
[Daniel comment: This is what Johannes and I experience with the Air Purifier’s we are testing that they “wash or scrub” the resident air leaving a nice feeling, smell-less air that seems clean and important being as we live in China with all that it brings.]
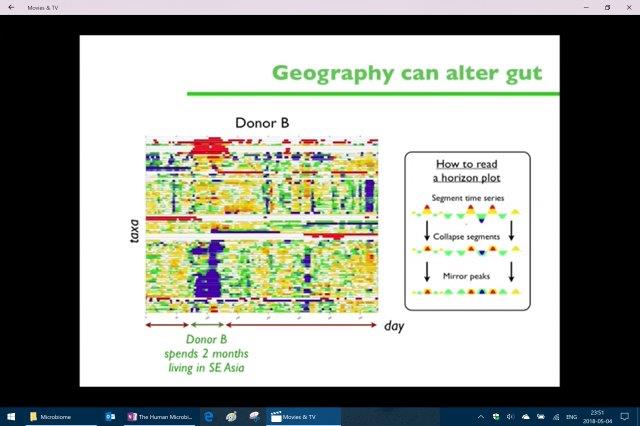
[The Human Microbiome – Eric Alm, PhD, Martin Blaser, MD, John Cryan, PhD, Rob Knight, PhD] 2013
(X-Axis is time and Y-Axis is Species) Here Eric Alm’s Human Gut Ecology Project Alm describes when his student went to Bangkok for a month during this study his microbiome changed almost immediately when arriving in Bangkok indicated in Red & Blue (different species) and almost immediately went back to normal when returning to the US.
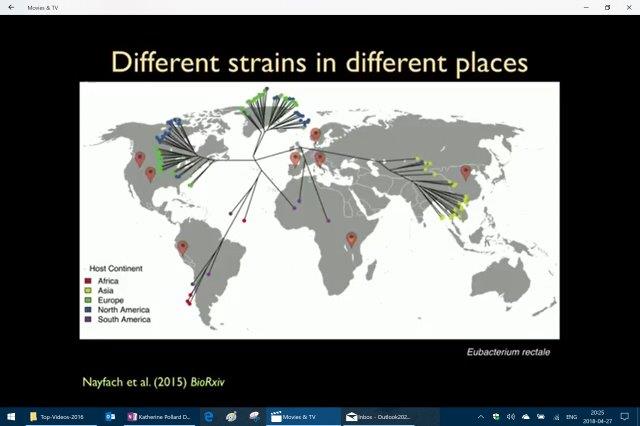
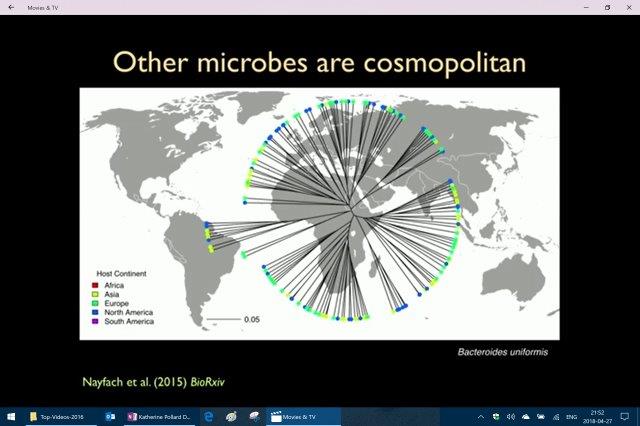
Above Katherine talks about very distinct strains of bacteria (Eubacterium rectale) and its presence in different countries and pointed out that Europe and NA show a little bit of a mix but in China and Africa very distinct. [37:33 min mark]
[In Katherine Pollard Massive Data Sheds Light on Your Microbiome _ Talks at Google at the 38 min mark discussing this map above finding a “geographic signal with microbes”]
Question:
If microbes are cosmopolitan, then what effect do they have on foreigners?
Are the microbes in China suitable to a white western foreigner? Could they be beneficial, strengthening our diversity or might they be unhealthy being species we didn’t evolve with and possibly messing up gene expression, digestion or immune system function?
Observation:
It seems that most the foreigners health appears to be deteriorate very fast. My personal health decline was dramatic but attribute a lot of cause to a problem with too much smoking and drinking. I also feel that China is hard on westerners for relatively poor food, water, air quality. The soils seem depleted with low biodiversity. Heavy air, light and noise pollution and negative environmental psychology all draw on our reserves now I am wondering about the effect of China microorganisms. Some microbiome research suggests that environment and geographic location harbor particular strains or species that may add a negative influence health to the western life?
My Family’s Microbiome Testing:

uBiome is a biotechnology company based in San Francisco that has developed key technology to sequence the human microbiomes. The company was founded by Jessica Richman and Zachary Apte who were scientists in the California Institute for Quantitative Biosciences. The company has proprietary machine learning algorithms that analyze the sequence data and compare it with the company’s proprietary database of microbiomes, built from the samples that partners and single customers send to them, and web-based software that allows individuals to view their microbiome and make certain comparisons. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UBiome>
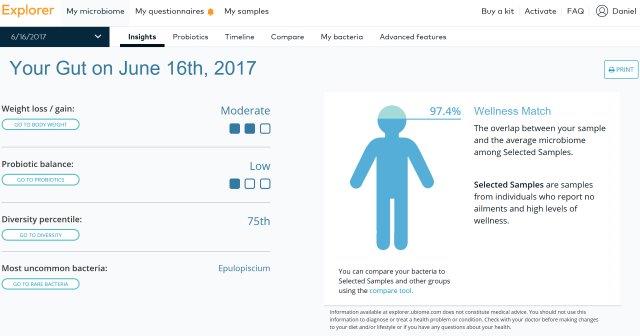
Purchased 3 Gut Kits for the family in 2016:
The kits were shipped to China no problem (empty) but after taking stool samples taken no shipping company would take them. Tried all shipping companies and various tricks but no go. Second samples taken using the spare tubes May 2017 and a friend took out of China them back and shipped to uBiome from Canada.
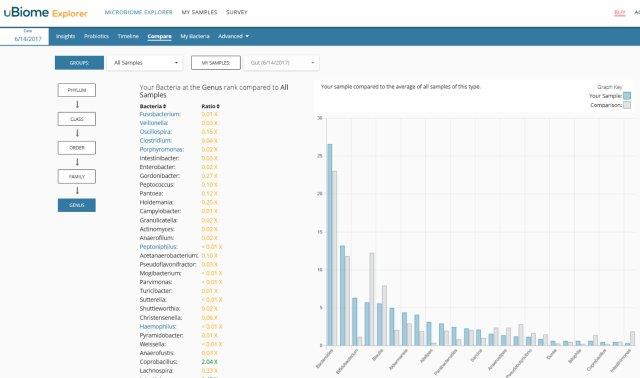
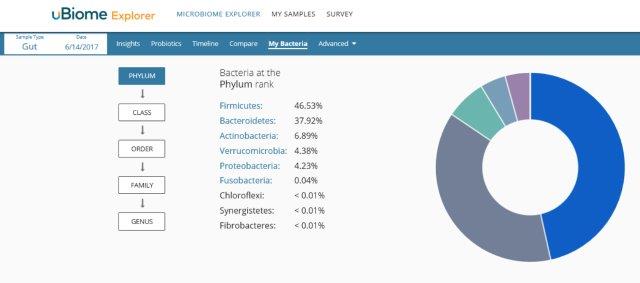
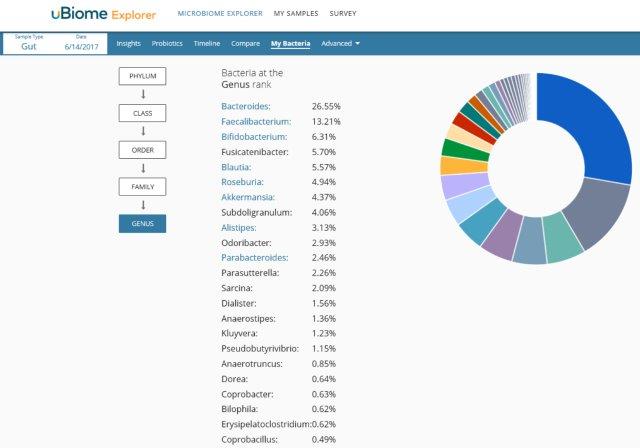
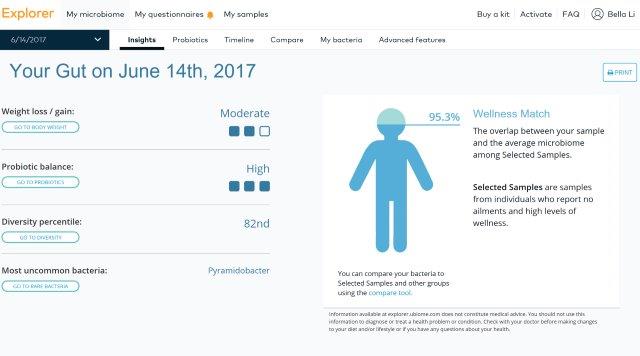
Comparative Data:
Comparing your sample compared to the average of all samples of this type.
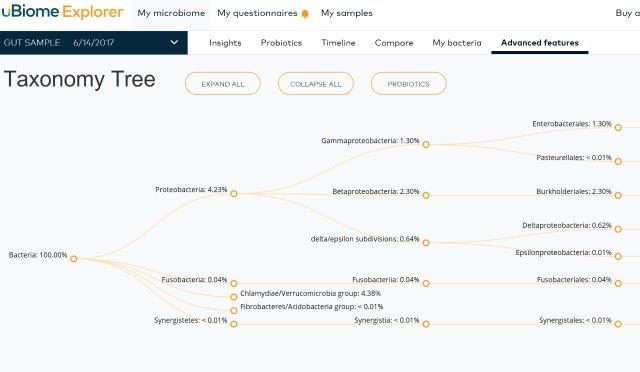
Some other cool features of uBiome dashboard:
Results from Study & Testing and Reality:
– All indicators show normal and comparable with the uBiome Database.
– Understanding the importance and role of the microbes we made adjustments and monitoring results.
– Diet changes
– Environment changes
– Continuous study and testing (Will get sampling done every few years, or if a major change in environment or health.)
Diet:
We have modified our diet to help stimulate or support our microbiome. Other than a good variety of foods as fresh as possible to including;
– Added a supplement Probiotic Ultra 25 Complex by GNC
– Found a nice new brand of juice claiming microorganisms.
– Switched to a Quality Aged Cheese
– Lot’s of Yoghurt
– Olives (Prefer fermented but settling for the vinegar preserved)
– Pickles (Prefer fermented but settling for the vinegar preserved)
– Fresh squeezed juice. (Multiple fruits)
– Need to focus on dietary fiber; clarify which are accessible, increase intake, and monitor.
Looking for but not able to find:
– Sauerkraut (fermented, non-vinegar)
– Peppers (fermented, non-vinegar)
– Onions (fermented, non-vinegar)
– Organic meats (frozen)
– Organic powders and or spices
– Would love to import some wild game meat from Canada. (Moose, Dear, Elk.) Anyone reading this with access to this kind of food I would be happy to import and distribute in China. (I have full capability.)
Environment:
The Ecosystem of the Built Environment (Our homes and offices where we spend most of our life.)


Being quite aware of this hypothesis:
– Changing of our washing and cleaning habits. No longer use any chemicals except a bit of bleach for known problems areas. (Dog pee/poo on floor and toilet, or if mold forms but don’t have that problem anymore.)
– Added lots of plants and animals with constant interaction.
– Get out to seaside and mountains and play in as much nature as we can although I very much doubt if the nature setting I can expose my family to are beneficial in this country because they seem so depleted of biodiversity with 5000 years of Chinese stomping around on it.
Continued Study & Observation:
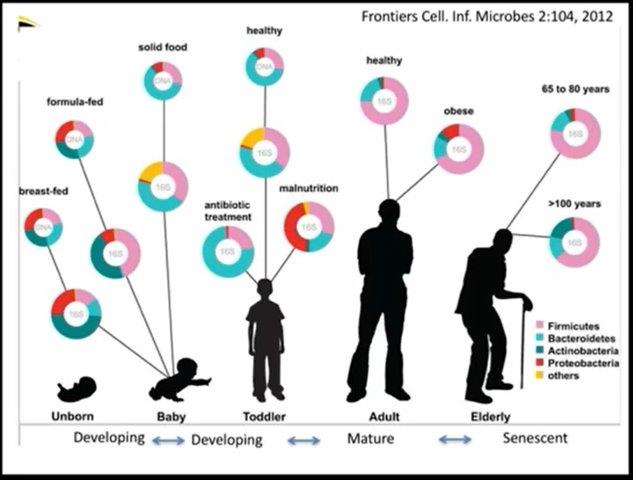
Because our microbiome changes with environment, diet, health and age;
– We will continuously get sampling done every few years, or if a major change in environment or health.
– We will continuously monitor our health, especially daughter for any of the modern diseases appearing so we can deal with them immediately.
Other Interesting Facts on the Microbiome
Evolving & Disappearing Microbes:

Martin Blaser has demonstrated that a particular taxa h.pylori has been with humans, 100% of humans for 100,000 years and has been on a slow decline to where now only 6% of children have this bacteria and appears it will be gone in a few generations.
Air Pollution & Pathogens:
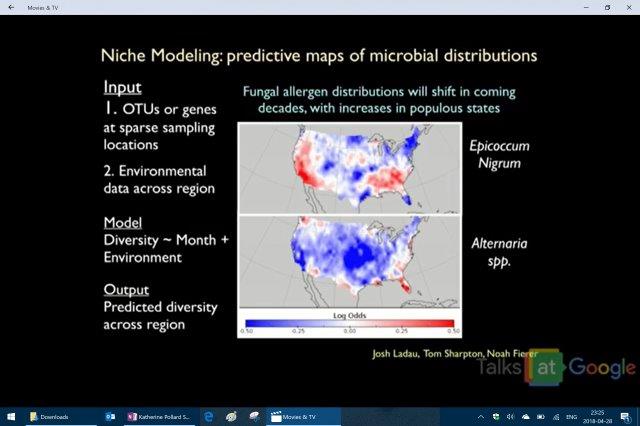
[Katherine Pollard Decoding the Human Microbiome]
[42 min mark] Katherine Pollard talks about as the earth warms (global warming) the microbes change and actually will like the warmer weather and that will have consequences for us. Pollard’s lab is starting to create models to do predictions with different parameters.
Fungal allergens in air will change as the climate changes (1000 homes project) and some pathogens like Epicoccum Nigrum a wicked pathogen that can kill immune deficient humans. Their model above shows the areas most affected in red.

“Microbiota molecules resemble that of drugs leaving us wonder about the effects they have on our bodies, moods, brains and diseases.”
Antibiotic Fed Animals
Martin Blaser made some interesting comments on the point of feeding our animals antibiotics to grow them fat so have to wonder about what is happening to our kids. We know that trace amount of those antibiotics remains in our foods so really should research what effect that is having if any.
Probiotics
Martin Blaser said right now, I’m actually a big believer in probiotics; I think that’s going to be part of the future of medicine, that we’re going to understand the science of the microbiome well enough so that we can look at a sample from a child and say this child is lacking such-and-such an organism and now we’re going to take it off the shelf and we’re going to give it back to that child. … Just as today the kids are lining up for the vaccines, in the future, maybe the kids are going to be drinking certain organisms so that we can replace the ones that they’ve lost. From <https://www.npr.org/2014/04/14/302899093/modern-medicine-may-not-be-doing-your-microbiome-any-favors>
Quorum Sensing


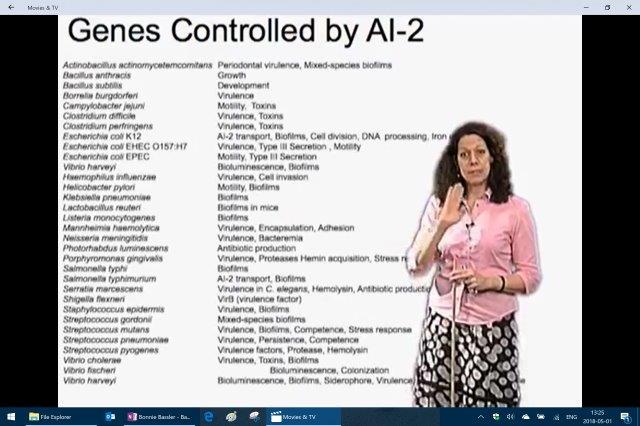
Bonnie Bassler and her lab is one of the leader in the understanding how bacteria communicate with each other and act as a group to affect us and our health. Bassler now claims that it is very clear that bacteria play an important role is gene control and or regulation as the above list demonstrates. (Bacteria on the left and gene function on right.)
State of the Science:

The above slide demonstrates the gaps or weakness in the microbiome studies:
– Most of the research is using mouse models, not humans. Despite the similarities we are very different.
– They are not able to really determine causality.
– There is much discussion about how and whether to treat the microbiome as another organ or organ system of the human body.
– Role of diet and interventions is still very unclear. [Daniel: Despite the numerous claims from entrepreneurs and their health products including probiotics.]
– The role of genetics and gene interaction still very unclear. [Daniel: Though there is lots of evidence that microbes do play a role in our gene of activating/deactivating and even gene regulation.]
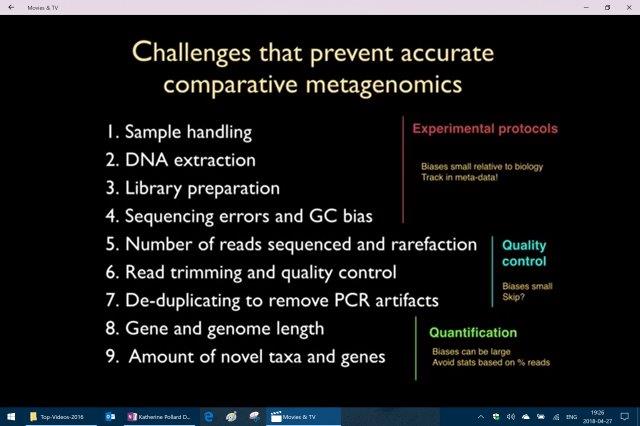
[Katherine Pollard Decoding the Human Microbiome] – 2016 Stanford School of Medicine
Talks about how “bias” affecting results and a huge need to be aware of that when looking at data. She lists many points that affect or prevent accuracy. For us laymen we need discernment, and realize without an understanding of how this science works we may read a paper thinking its accurate when in fact it is not. (Many factors influence accuracy including bias on reading data, sample quality, sample size, contamination, and many other factors would be critical to understand the knowledge obtained.)
[Daniel comments: Other science I have watched showed how in the past scientific papers produced by reputable scientists and qualified labs published in top peer reviewed journals have come out with things like “scientists have identified the gene for “obesity, speech, diabetes, on and on” only to find out later that is simply not 100% accurate.]
Leading scientists say the media has mislead us and it is much more complex than being able to point to a single gene and make claims. We now have expanded our understanding and realize multiple genes, environment and now random chance all play a significant role let alone the interaction with the millions of genes and cells from of our microbiome. (Robert Sapolsky – The traditional “Nature vs. Nurture” debate now has a third component of chance. Random chance is now playing a strong role making behavior much more complex increasing variability.)]
Comments on Microbiome Company Ethics/Claims:
Erica Sonnenburg said that she has seen some unbelievable claims from some of these companies. One she says claimed to make a custom Probiotic based on your microbiome which she says is absurd, and has no idea where they get that information from because she and her lab think that is impossible at the current state of knowledge.
Resources:
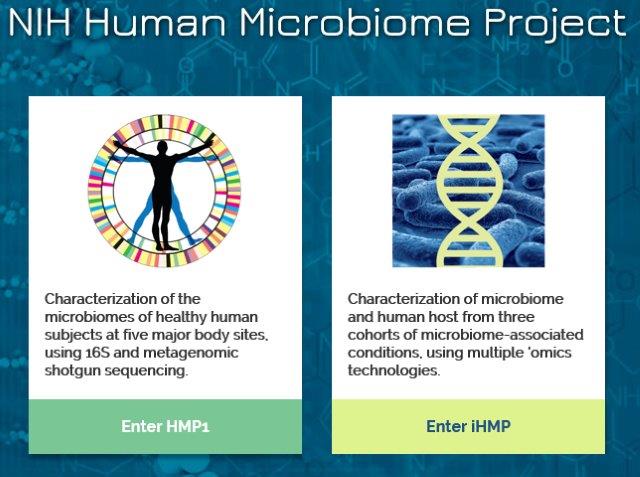
The Human Microbiome Project (HMP) [https://hmpdacc.org/]
The Human Microbiome Project (HMP) was a United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) research initiative to improve understanding of the microbial flora involved in human health and disease. Launched in 2008, the first phase (HMP1) was a five-year project that focused on identifying and characterizing human microbial flora. The second phase, known as the Integrative Human Microbiome Project (iHMP) launched in 2014 with the aim of generating resources to characterize the microbiome and elucidating the roles of microbes in health and disease states. From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_Microbiome_Project>
HMP results from the now completed 10 years project reported to the National Advisory Council for Human Genome Research committee meeting.
– [NIH Human Microbiome Project An Update – Eric Green 2013]
– [The Human Microbiome Project – Lita Proctor]
– [The Human Microbiome Project – Lita Proctor PPT Slides 2018-02-06.pdf]
Bonnie Lynn Bassler, Ph.D is an American molecular biologist. She has been a professor at Princeton University since 1994. In 2002, she was awarded a MacArthur Fellowship. She has won the Wiley prize in Biomedical Sciences in 2009 for “pioneering investigations of quorum sensing, a mechanism that allows bacteria to “talk” to each other to coordinate their behavior, even between species.
Bassler’s Lectures:
– [The Secret Language of Bacteria – An ASM Microbes After Hours Event]
– [Bonnie Bassler-How bacteria talk-TedTalk]
– [Bonnie Bassler (Princeton) Part 1 Bacterial Communication via Quorum Sensing]
– [Bonnie Bassler (Princeton) Part 2 Vibrio Cholerae Quorum Sensing and Novel Antibiotics]
Rob Knight:
Rob Knight is a professor at the University of California, San Diego and the co-founder of the American Gut Project. he is also a co-founder of the Earth Microbiome Project. His lab’s research involves the development of laboratory and computational techniques to characterize the microbiomes of humans, animals, and the environment.
– [Rob Knight How our microbes make us who we are – TED Talk]
– [From the Human Microbiome Project to the Earth Microbiome Project – Rob Knight]
– [Establishing causality in microbiome studies – Rob Knight 2017]
Justin & Erica Sonnenburg:
– [Understanding The Microbiome, Erica Sonnenburg, PhD]
– [Your Microbiome What Is It, and How Can It Help or Hurt You]
Katherine Pollard:
– [Understanding The Microbiome, Erica Sonnenburg, PhD]
– [Your Microbiome What Is It, and How Can It Help or Hurt You]
Katherine Pollard:
[Katherine Pollard Decoding the Human Microbiome]
2016 Stanford School of Medicine:
Now a shotgun approach obtaining multiple sequences (Huge text file: 50 million 100-letter long sequences) has enabled scientists to identify the species of organisms that wasn’t possible just 5 years ago.
[Claire Fraser – The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease]
Excellent and informative lecture by another leader in the field. Very good for a layperson to get a general understanding of the Microbiome.
[The Human Microbiome – Eric Alm, PhD, Martin Blaser, MD, John Cryan, PhD, Rob Knight, PhD]
Four big names with Microbiome Research each present a short talk then a Q&A panel discussion.
[Close Friends The Microbiome and the Immune System]
Gastrologist Susan Lynch PhD describes the connection between our microbiome and our immune system.
[The Evolving Human Microbiome]
Dr. Alexander Khoruts MD presents and excellent lecture on the Evolving Microbiome and the new frontier in medical therapeutical applications.
[Ashlee Earl Why Microbes Matter]
[Ashlee Earl The Face of Bacillus Subtilis Genomes and Biofilms] 2008
The first talk is an excellent presentation for laypeople to get to know and better understand the microbiome. The second talk a little more focused on the bacteria of her research. Both excellent talks.

[Dianne Newman (CalTech) Part 1 An Overview of Microbial Diversity and Evolution]
[Dianne Newman (CalTech) Part 2 Microbial Respiration of Arsenate]
[Dianne Newman (CalTech) Part 3 Interpreting Molecular Fossils of Oxygenic Photosynthesis]
Built Environment:
In social science, the term built environment, or built world, refers to the human-made surroundings that provide the setting for human activity, ranging in scale from buildings to parks. It has been defined as “the human-made space in which people live, work, and recreate on a day-to-day basis.” From <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Built_environment>
[Jessica Green The Ecology of Indoor Environments]
[Jessica Green Good germs make healthy buildings – TED Talk]
Jessica studies the relationship of the microbial community in our even more sealed and controlled indoor environments called “the built environment”.
[Brent Stephens – Perspectives on Microbial Interactions in Built Environments]
Brent looks at the literature regarding the role of the built environment, microbes and human health citing many of the latest studies in the field so an excellent resource for better understanding microbes in the built environment and the studies associated.
[Unimaginable, unprecedented, microbial diversity by Professor Jim Prosser]
Jim Prosser speaking on the abundance and complexity of the microbes that make up our earths soils, and their role in the PH and nitrification.




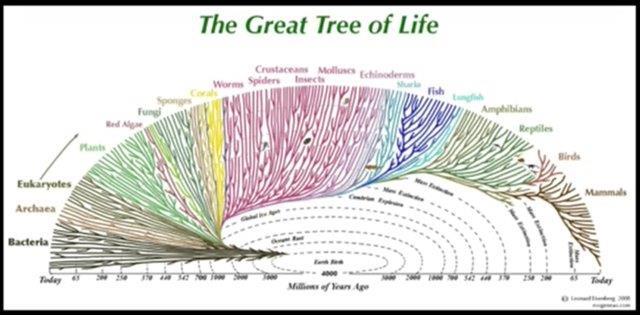
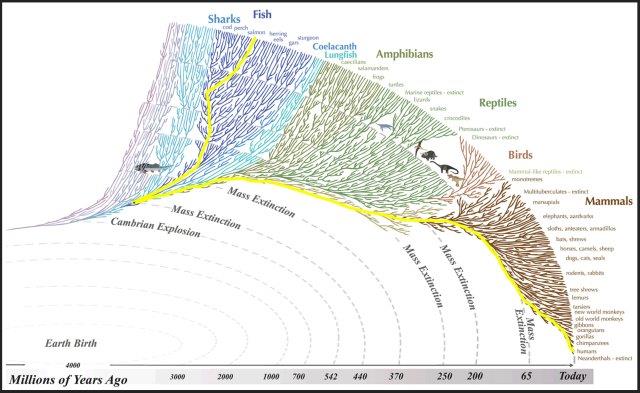
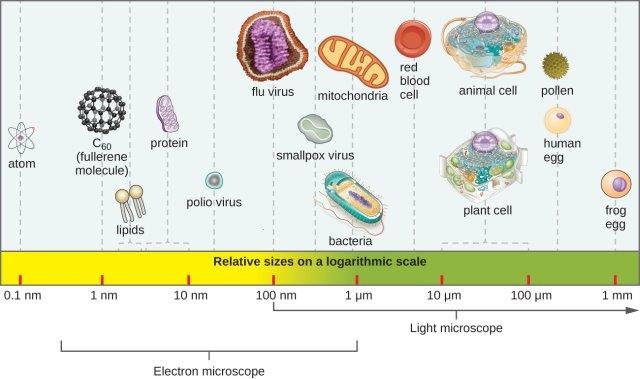







Definitions key to discussions: